HAEM5:Acute myeloid leukaemia with CBFB::MYH11 fusion: Difference between revisions
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
No edit summary |
Bailey.Glen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Acute myeloid leukaemia with CBFB::MYH11 fusion}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Acute myeloid leukaemia with CBFB::MYH11 fusion}} | ||
[[HAEM5:Table_of_Contents|Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)]] | [[HAEM5:Table_of_Contents|Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)]] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA | Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA | ||
==WHO Classification of Disease== | ==WHO Classification of Disease== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 36: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Related Terminology== | ==Related Terminology== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
|Acceptable | |Acceptable | ||
| | |Acute myeloid leukaemia with CBFB rearrangement; acute myeloid leukaemia with t(16;16)(p13.1;q22); acute myeloid leukaemia with inv(16)(p13.1q22) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Not Recommended | |Not Recommended | ||
| | |N/A | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 124: | Line 106: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
Put content below into table above... | |||
* | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 160: | Line 145: | ||
*Standard induction 7 + 3 chemotherapy regimen of cytarabine for 7 days plus an anthracycline or anthracenedione for 3 days. In first complete remission patients younger than 60 years without a KIT mutation are treated with at least three courses of high dose cytarabine. If a ''KIT'' mutation is present, bone marrow transplant is performed in first complete remission<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Yoon|first=J.-H.|last2=Kim|first2=H.-J.|last3=Kim|first3=J.-W.|last4=Jeon|first4=Y.-W.|last5=Shin|first5=S.-H.|last6=Lee|first6=S.-E.|last7=Cho|first7=B.-S.|last8=Eom|first8=K.-S.|last9=Kim|first9=Y.-J.|date=2014-12|title=Identification of molecular and cytogenetic risk factors for unfavorable core-binding factor-positive adult AML with post-remission treatment outcome analysis including transplantation|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25111512|journal=Bone Marrow Transplantation|volume=49|issue=12|pages=1466–1474|doi=10.1038/bmt.2014.180|issn=1476-5365|pmid=25111512}}</ref>. Other therapies under investigation include gemtuzumab ozogamicin, histone deacetylase inhibitors, DNA methyl transferase inhibitors, proteasome inhibition and tyrosine kinase inhibitors<ref name=":1" />. | *Standard induction 7 + 3 chemotherapy regimen of cytarabine for 7 days plus an anthracycline or anthracenedione for 3 days. In first complete remission patients younger than 60 years without a KIT mutation are treated with at least three courses of high dose cytarabine. If a ''KIT'' mutation is present, bone marrow transplant is performed in first complete remission<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Yoon|first=J.-H.|last2=Kim|first2=H.-J.|last3=Kim|first3=J.-W.|last4=Jeon|first4=Y.-W.|last5=Shin|first5=S.-H.|last6=Lee|first6=S.-E.|last7=Cho|first7=B.-S.|last8=Eom|first8=K.-S.|last9=Kim|first9=Y.-J.|date=2014-12|title=Identification of molecular and cytogenetic risk factors for unfavorable core-binding factor-positive adult AML with post-remission treatment outcome analysis including transplantation|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25111512|journal=Bone Marrow Transplantation|volume=49|issue=12|pages=1466–1474|doi=10.1038/bmt.2014.180|issn=1476-5365|pmid=25111512}}</ref>. Other therapies under investigation include gemtuzumab ozogamicin, histone deacetylase inhibitors, DNA methyl transferase inhibitors, proteasome inhibition and tyrosine kinase inhibitors<ref name=":1" />. | ||
|} | |}[[File:t(16;16)(p13.1;q22).png|t(16;16)(p13.1;q22)|frame|alt=|left]] [[File:inv(16)(p13.1q22).png|inv(16)(p13.1q22)|frame|alt=|left]] [[File:Inv(16)(p13.1q22) karyogram and insert (8-7-18).png|inv(16)(p13.1q22). Courtesy of Karen Kundinger, Comprehensive Genetic Services, Milwaukee, WI|frame|alt=|none]] | ||
inv(16)(p13.1q22), a pericentric inversion of chromosome 16, and the less common t(16;16)(p13.1;q22), a translocation involving the short arm of one chromosome 16 and the long arm of the other chromosome 16, define a distinctive cytogenetic subtype of acute myeloid leukemia. Both of these chromosome rearrangements result in the CBFB-MYH11 gene fusion. | |||
* | |||
==Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH== | ==Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH== | ||
| Line 166: | Line 156: | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Chr #!! | !Chr #!!Gain, Loss, Amp, LOH!!Minimal Region Cytoband and/or Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build; Size]!!Relevant Gene(s) | ||
! | !Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | ||
! | !Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | ||
! | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| Line 271: | Line 261: | ||
!Chromosomal Pattern | !Chromosomal Pattern | ||
!Molecular Pathogenesis | !Molecular Pathogenesis | ||
! | !Prevalence - | ||
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | |||
! | !Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | ||
! | !Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | ||
! | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> | ||
| Line 324: | Line 314: | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Gene!! | !Gene!!Genetic Alteration!!Tumor Suppressor Gene, Oncogene, Other!!Prevalence - | ||
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | |||
! | !Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | ||
! | !Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | ||
! | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
|<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span>''EGFR'' | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span>''EGFR'' | ||
| Line 370: | Line 360: | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Gene; Genetic Alteration!! | !Gene; Genetic Alteration!!Presumed Mechanism (Tumor Suppressor Gene [TSG] / Oncogene / Other)!!Prevalence (COSMIC / TCGA / Other)!!Concomitant Mutations!!Mutually Exclusive Mutations | ||
! | !Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | ||
!Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | !Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | ||
!Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | !Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | ||
| Line 480: | Line 470: | ||
The <u>epidemiology/prevalence</u> of this disease is detailed below: | The <u>epidemiology/prevalence</u> of this disease is detailed below: | ||
* Approximately 5-8% of AML cases have inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22). More common in males and younger adults. | *Approximately 5-8% of AML cases have inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22). More common in males and younger adults. | ||
The <u>clinical features</u> of this disease are detailed below: | The <u>clinical features</u> of this disease are detailed below: | ||
| Line 490: | Line 480: | ||
The <u>sites of involvement</u> of this disease are detailed below: | The <u>sites of involvement</u> of this disease are detailed below: | ||
* Bone marrow | *Bone marrow | ||
The <u>morphologic features</u> of this disease are detailed below: | The <u>morphologic features</u> of this disease are detailed below: | ||
| Line 515: | Line 505: | ||
*populations with granulocytic differentiation positive for CD13, CD33, CD15, CD65 and MPO | *populations with granulocytic differentiation positive for CD13, CD33, CD15, CD65 and MPO | ||
*populations with monocytic differentiation, positive for CD14, CD4, CD11c, CD11b, CD11c, CD64, CD36 and lysozyme | *populations with monocytic differentiation, positive for CD14, CD4, CD11c, CD11b, CD11c, CD64, CD36 and lysozyme | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 3 July 2025
Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)
| This page is under construction |
editContent Update To WHO 5th Edition Classification Is In Process; Content Below is Based on WHO 4th Edition ClassificationThis page was converted to the new template on 2023-12-07. The original page can be found at HAEM4:Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22); CBFB-MYH11.
(General Instructions – The focus of these pages is the clinically significant genetic alterations in each disease type. This is based on up-to-date knowledge from multiple resources such as PubMed and the WHO classification books. The CCGA is meant to be a supplemental resource to the WHO classification books; the CCGA captures in a continually updated wiki-stye manner the current genetics/genomics knowledge of each disease, which evolves more rapidly than books can be revised and published. If the same disease is described in multiple WHO classification books, the genetics-related information for that disease will be consolidated into a single main page that has this template (other pages would only contain a link to this main page). Use HUGO-approved gene names and symbols (italicized when appropriate), HGVS-based nomenclature for variants, as well as generic names of drugs and testing platforms or assays if applicable. Please complete tables whenever possible and do not delete them (add N/A if not applicable in the table and delete the examples); to add (or move) a row or column in a table, click nearby within the table and select the > symbol that appears. Please do not delete or alter the section headings. The use of bullet points alongside short blocks of text rather than only large paragraphs is encouraged. Additional instructions below in italicized blue text should not be included in the final page content. Please also see Author_Instructions and FAQs as well as contact your Associate Editor or Technical Support.)
Primary Author(s)*
Christine Bryke, MD
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA
WHO Classification of Disease
| Structure | Disease |
|---|---|
| Book | Haematolymphoid Tumours (5th ed.) |
| Category | Myeloid proliferations and neoplasms |
| Family | Acute myeloid leukaemia |
| Type | Acute myeloid leukaemia with defining genetic abnormalities |
| Subtype(s) | Acute myeloid leukaemia with CBFB::MYH11 fusion |
Related Terminology
| Acceptable | Acute myeloid leukaemia with CBFB rearrangement; acute myeloid leukaemia with t(16;16)(p13.1;q22); acute myeloid leukaemia with inv(16)(p13.1q22) |
| Not Recommended | N/A |
Gene Rearrangements
Put your text here and fill in the table (Instructions: Details on clinical significance such as prognosis and other important information can be provided in the notes section. Please include references throughout the table. Do not delete the table.)
| Driver Gene | Fusion(s) and Common Partner Genes | Molecular Pathogenesis | Typical Chromosomal Alteration(s) | Prevalence -Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE: ABL1 | EXAMPLE: BCR::ABL1 | EXAMPLE: The pathogenic derivative is the der(22) resulting in fusion of 5’ BCR and 3’ABL1. | EXAMPLE: t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) | EXAMPLE: Common (CML) | EXAMPLE: D, P, T | EXAMPLE: Yes (WHO, NCCN) | EXAMPLE:
The t(9;22) is diagnostic of CML in the appropriate morphology and clinical context (add reference). This fusion is responsive to targeted therapy such as Imatinib (Gleevec) (add reference). BCR::ABL1 is generally favorable in CML (add reference). |
| EXAMPLE: CIC | EXAMPLE: CIC::DUX4 | EXAMPLE: Typically, the last exon of CIC is fused to DUX4. The fusion breakpoint in CIC is usually intra-exonic and removes an inhibitory sequence, upregulating PEA3 genes downstream of CIC including ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5. | EXAMPLE: t(4;19)(q25;q13) | EXAMPLE: Common (CIC-rearranged sarcoma) | EXAMPLE: D | EXAMPLE:
DUX4 has many homologous genes; an alternate translocation in a minority of cases is t(10;19), but this is usually indistinguishable from t(4;19) by short-read sequencing (add references). | |
| EXAMPLE: ALK | EXAMPLE: ELM4::ALK
|
EXAMPLE: Fusions result in constitutive activation of the ALK tyrosine kinase. The most common ALK fusion is EML4::ALK, with breakpoints in intron 19 of ALK. At the transcript level, a variable (5’) partner gene is fused to 3’ ALK at exon 20. Rarely, ALK fusions contain exon 19 due to breakpoints in intron 18. | EXAMPLE: N/A | EXAMPLE: Rare (Lung adenocarcinoma) | EXAMPLE: T | EXAMPLE:
Both balanced and unbalanced forms are observed by FISH (add references). | |
| EXAMPLE: ABL1 | EXAMPLE: N/A | EXAMPLE: Intragenic deletion of exons 2–7 in EGFR removes the ligand-binding domain, resulting in a constitutively active tyrosine kinase with downstream activation of multiple oncogenic pathways. | EXAMPLE: N/A | EXAMPLE: Recurrent (IDH-wildtype Glioblastoma) | EXAMPLE: D, P, T | ||
Put content below into table above...
| Chromosomal Rearrangement | Genes in Fusion (5’ or 3’ Segments) | Pathogenic Derivative | Prevalence | Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) | 5'CBFB / 3'MYH11 | der(16) | 5-8% of AML | Yes | Yes | No | Diagnostic
Per 2022 International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias guidelines, blast count needs to be at least 10% or more [1]
|
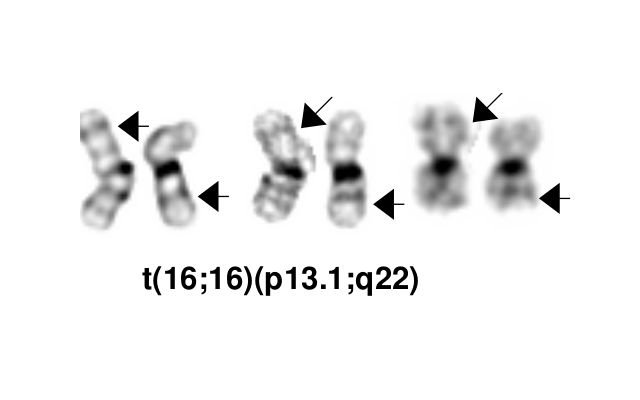
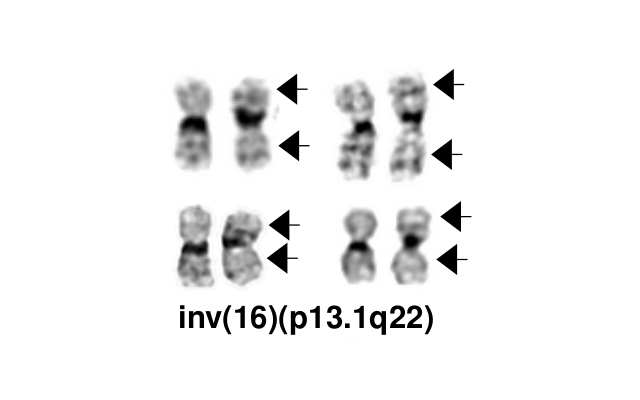
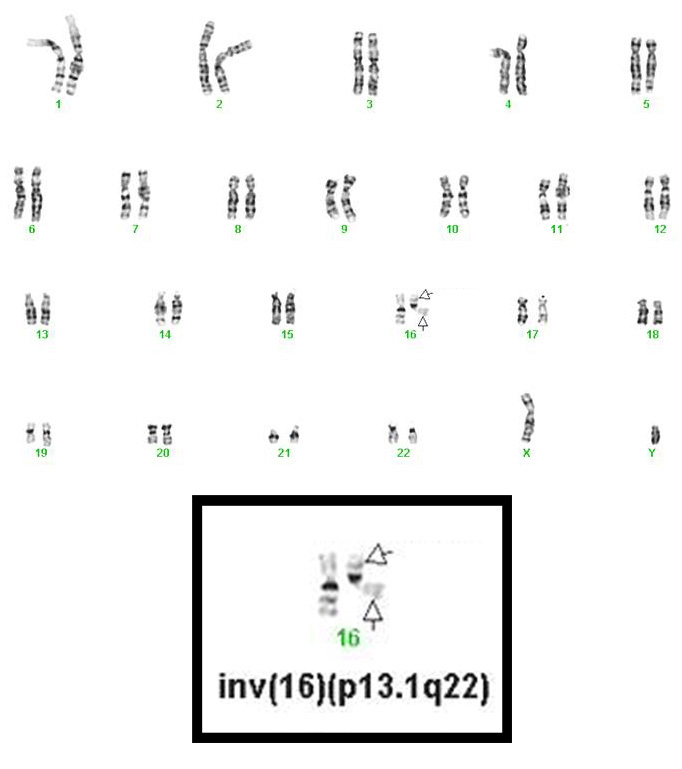
inv(16)(p13.1q22), a pericentric inversion of chromosome 16, and the less common t(16;16)(p13.1;q22), a translocation involving the short arm of one chromosome 16 and the long arm of the other chromosome 16, define a distinctive cytogenetic subtype of acute myeloid leukemia. Both of these chromosome rearrangements result in the CBFB-MYH11 gene fusion.
Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH
Put your text here and fill in the table (Instructions: Includes aberrations not involving gene rearrangements. Details on clinical significance such as prognosis and other important information can be provided in the notes section. Can refer to CGC workgroup tables as linked on the homepage if applicable. Please include references throughout the table. Do not delete the table.)
| Chr # | Gain, Loss, Amp, LOH | Minimal Region Cytoband and/or Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build; Size] | Relevant Gene(s) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE:
7 |
EXAMPLE: Loss | EXAMPLE:
chr7 |
EXAMPLE:
Unknown |
EXAMPLE: D, P | EXAMPLE: No | EXAMPLE:
Presence of monosomy 7 (or 7q deletion) is sufficient for a diagnosis of AML with MDS-related changes when there is ≥20% blasts and no prior therapy (add reference). Monosomy 7/7q deletion is associated with a poor prognosis in AML (add references). |
| EXAMPLE:
8 |
EXAMPLE: Gain | EXAMPLE:
chr8 |
EXAMPLE:
Unknown |
EXAMPLE: D, P | EXAMPLE:
Common recurrent secondary finding for t(8;21) (add references). | |
| EXAMPLE:
17 |
EXAMPLE: Amp | EXAMPLE:
17q12; chr17:39,700,064-39,728,658 [hg38; 28.6 kb] |
EXAMPLE:
ERBB2 |
EXAMPLE: D, P, T | EXAMPLE:
Amplification of ERBB2 is associated with HER2 overexpression in HER2 positive breast cancer (add references). Add criteria for how amplification is defined. | |
inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) is the sole chromosome aberration in approximately 60% of cases.
| Chr # | Gain / Loss / Amp / LOH | Minimal Region Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build] | Minimal Region Cytoband | Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | Gain | chr8:1-145,138,636 [hg38] | chr8 | No | No | No | Frequently observed. Does not adversely affect the favorable prognosis associated with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) unless a KIT gene mutation is also present (see below) |
| 22 | Gain | chr22:1-50,818,468 [hg38] | chr22 | No | No | No | Frequently observed. Does not adversely affect the favorable prognosis associated with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) unless a KIT gene mutation is also present (see below) |
| 21 | Gain | chr21:1-46,709,983 [hg38] | chr21 | No | No | No | Occasionally observed. Does not adversely affect the favorable prognosis associated with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) unless a KIT gene mutation is also present (see below) |
| 7 | Loss | chr7:60,100,001-159,345,973 [hg38] | chr7q | No | No | No | Occasionally observed. Does not adversely affect the favorable prognosis associated with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) unless a KIT gene mutation is also present (see below) |
Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns
Put your text here and fill in the table (Instructions: Included in this category are alterations such as hyperdiploid; gain of odd number chromosomes including typically chromosome 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, and 17; co-deletion of 1p and 19q; complex karyotypes without characteristic genetic findings; chromothripsis; microsatellite instability; homologous recombination deficiency; mutational signature pattern; etc. Details on clinical significance such as prognosis and other important information can be provided in the notes section. Please include references throughout the table. Do not delete the table.)
| Chromosomal Pattern | Molecular Pathogenesis | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE:
Co-deletion of 1p and 18q |
EXAMPLE: See chromosomal rearrangements table as this pattern is due to an unbalanced derivative translocation associated with oligodendroglioma (add reference). | EXAMPLE: Common (Oligodendroglioma) | EXAMPLE: D, P | ||
| EXAMPLE:
Microsatellite instability - hypermutated |
EXAMPLE: Common (Endometrial carcinoma) | EXAMPLE: P, T | |||
editv4:Characteristic Chromosomal PatternsThe content below was from the previous version of the page. Please incorporate above.
| Chromosomal Pattern | Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Applicable | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
End of V4 Section
Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)
Put your text here and fill in the table (Instructions: This table is not meant to be an exhaustive list; please include only genes/alterations that are recurrent or common as well either disease defining and/or clinically significant. If a gene has multiple mechanisms depending on the type or site of the alteration, add multiple entries in the table. For clinical significance, denote associations with FDA-approved therapy (not an extensive list of applicable drugs) and NCCN or other national guidelines if applicable; Can also refer to CGC workgroup tables as linked on the homepage if applicable as well as any high impact papers or reviews of gene mutations in this entity. Details on clinical significance such as prognosis and other important information such as concomitant and mutually exclusive mutations can be provided in the notes section. Please include references throughout the table. Do not delete the table.)
| Gene | Genetic Alteration | Tumor Suppressor Gene, Oncogene, Other | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE:EGFR
|
EXAMPLE: Exon 18-21 activating mutations | EXAMPLE: Oncogene | EXAMPLE: Common (lung cancer) | EXAMPLE: T | EXAMPLE: Yes (NCCN) | EXAMPLE: Exons 18, 19, and 21 mutations are targetable for therapy. Exon 20 T790M variants cause resistance to first generation TKI therapy and are targetable by second and third generation TKIs (add references). |
| EXAMPLE: TP53; Variable LOF mutations
|
EXAMPLE: Variable LOF mutations | EXAMPLE: Tumor Supressor Gene | EXAMPLE: Common (breast cancer) | EXAMPLE: P | EXAMPLE: >90% are somatic; rare germline alterations associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (add reference). Denotes a poor prognosis in breast cancer. | |
| EXAMPLE: BRAF; Activating mutations | EXAMPLE: Activating mutations | EXAMPLE: Oncogene | EXAMPLE: Common (melanoma) | EXAMPLE: T | ||
Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in cBioportal, COSMIC, and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content.
AML with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) has genetic heterogeneity at the molecular level. Several genes have been identified that are frequently mutated in this subset of AML, some of them adversely affecting prognosis.
| Gene; Genetic Alteration | Presumed Mechanism (Tumor Suppressor Gene [TSG] / Oncogene / Other) | Prevalence (COSMIC / TCGA / Other) | Concomitant Mutations | Mutually Exclusive Mutations | Diagnostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Prognostic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Therapeutic Significance (Yes, No or Unknown) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KIT; Gain of Function mutations in exons 8 or 17 | Proto-Oncogene | 30%[2] | N/A | N/A | No | Yes | The KIT gene on 4q12 encodes a transmembrane glycoprotein that activates signaling pathways involved in cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival. Associated with a high risk of relapse in cases of AML with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22). Patients with KIT mutations have a significantly shorter overall survival and disease free survival periods than those without KIT mutations. Gene expression profile analysis of KIT mutation positive core binding factor AML showed dysregulation of genes belonging to the NF-κB signaling complex indicating impairment of apoptosis[5]. |
Other Mutations
Mutations in NRAS (45%), KRAS and FLT3 (FLT3-TKD and FLT3-ITD) have also been found in inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) AML[6]. Recently a FLT3 N676K mutation has been identified in a small subset of the disease[7][8]. In addition, TET2 mutations have been identified[9] and WT1 mutations have been found to be relatively common (13.8%) in inv(16) core-binding factor leukemia[10]. CBL mutations are less common and can be seen in ~5% of patients with inv(16) AML[11].
- Negative for ASXL2 mutation [which is common in t(8;21)].
Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in cBioportal (https://www.cbioportal.org/), COSMIC (https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic), ICGC (https://dcc.icgc.org/) and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content.
Epigenomic Alterations
None
Genes and Main Pathways Involved
Put your text here and fill in the table (Instructions: Please include references throughout the table. Do not delete the table.)
| Gene; Genetic Alteration | Pathway | Pathophysiologic Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| EXAMPLE: BRAF and MAP2K1; Activating mutations | EXAMPLE: MAPK signaling | EXAMPLE: Increased cell growth and proliferation |
| EXAMPLE: CDKN2A; Inactivating mutations | EXAMPLE: Cell cycle regulation | EXAMPLE: Unregulated cell division |
| EXAMPLE: KMT2C and ARID1A; Inactivating mutations | EXAMPLE: Histone modification, chromatin remodeling | EXAMPLE: Abnormal gene expression program |
editv4:Genes and Main Pathways InvolvedThe content below was from the previous version of the page. Please incorporate above.
CBFB (core binding factor β) on 16q22 is transcribed from centromere to telomere. It codes for CBFβ, a subunit of the transcription factor complex core binding factor. CBFβ by itself does not contain any DNA binding motif or transcriptional activation domain, but forms a dimer with CBFa (RUNX1) which is a transcription factor . MYH11 (smooth muscle myosin heavy-chain gene) on 16p13.1 is transcribed from centromere to telomere, contains a N-term ATPase head responsible for actin binding and mechanical movement, and a C-terminus long repeat of coil-coil domain to facilitate filament aggregates; member of the myosin II family.
DNA: inv(16)(p13.1q22) and t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) result in the CBFB-MYH11 hybrid gene involving fusion of 5’ CBFB in intron 5 and variable breakpoints in MYH11.
mRNA: At least 8 different CBFB-MYH11 fusion transcripts have been described. A transcript with CBFB and MYH11 positions at nucleotides 495 and 1921, respectively, is found in about 90% of patients. There is no reciprocal MYH11-CBFB transcript.
Protein: A fusion protein with the first 165 (or 133 in a few cases) amino acids of the N-terminus of CBFβ, minus only 17 or 22 amino acids, fused to the tail of the MYH11 C-terminus with its multimerization domain. The breakpoint in MYH11 is variable. The fusion protein retains the ability to dimerize with RUNX1 in the heterodimeric core binding factor. The core binding factor is a transcription factor that plays an essential role in regulation of normal hematopoiesis. It is composed of a DNA-binding CBFα (RUNX1) chain and a non-DNA-binding CBFβ chain. It is likely oncogenic due to altered transcriptional regulation of normal RUNX1 target genes. Animal studies suggest that the fusion proteins alone are not able to induce leukemia and that additional genetic alterations are required for leukemogenic transformation[12].
End of V4 Section
Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods
Chromosome analysis for inversion or translocation; FISH or RT-PCR for CBFB-MYH11 gene fusion rearrangement.
FISH or RT-PCR for CBFB-MYH11 is needed when chromosome morphology is suboptimal and for cytogenetically cryptic cases with typical bone marrow morphology and immunophenotype.
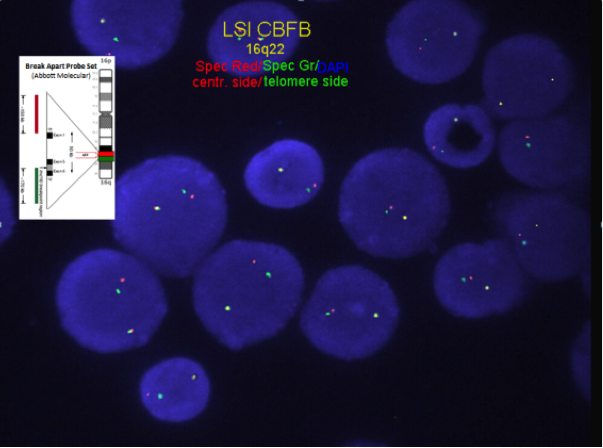
- RT-PCR for CBFB-MYH11 is employed for minimal residual disease detection. The attainment of optimal PCR response (OPR) of <0.1% PCR transcripts (at a level of detection of 10-4 ) after induction (C1) and <0.01% during or following consolidation has led to improved relapse-free survival (RFS)[13][14]
- In KIT mutation positive cases detection of the KIT mutation should not be used for assessment minimal residual disease because KIT mutations are frequently lost at relapse[11].
Familial Forms
None
Additional Information
This disease is defined/characterized as detailed below:
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) resulting in CBFB-MYH11 gene fusion is a subtype of AML with granulocytic and monocytic differentiation and abnormal bone marrow eosinophils. In the 2016 revision to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia, it is in the group of AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities[15]. In the older French-American-British (FAB) classification system, inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) positive AML belonged to the acute myelomonocytic leukemia with abnormal bone marrow eosinophils M4e category. inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) can occasionally be seen in therapy-related AML and in blast phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia. In those instances, the leukemia is not classified in the group of AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities due to clinical and prognostic differences.
- inv(16)(p13.1q22), a pericentric inversion of chromosome 16, and the less common t(16;16)(p13.1;q22), a translocation involving the short arm of one chromosome 16 and the long arm of the other chromosome 16, define a distinctive cytogenetic subtype of acute myeloid leukemia. Both of these chromosome rearrangements result in the CBFB-MYH11 gene fusion.
- Occurs in all age groups but predominantly in younger patients.
- Myeloid sarcoma may be present at initial diagnosis or at relapse and in some patients may constitute the only evidence of relapse.
- inv(16)(p13.1q22) is a subtle chromosome rearrangement that may not be appreciated when chromosome morphology is suboptimal.
- Cases with a cryptic CBFB-MYH11 gene rearrangement are possible.
- A deletion within 16p13 accompanying a rearrangement of 16p13 and 16q22 occurs in 20% of cases[16][17].
- Loss of 3’ CBFB occurs in 4-8% of cases of CBFB rearranged AML. Of these cases, 69-73% are positive for CBFB-MYH11 fusion by RT-PCR [18][19][20][21].
The epidemiology/prevalence of this disease is detailed below:
- Approximately 5-8% of AML cases have inv(16)(p13.1q22) or t(16;16)(p13.1;q22). More common in males and younger adults.
The clinical features of this disease are detailed below:
Signs and symptoms - May present as myeloid sarcoma
Laboratory findings - Abnormal eosinophil component (bone marrow); Leukocytosis
The sites of involvement of this disease are detailed below:
- Bone marrow
The morphologic features of this disease are detailed below:
- Bone marrow shows the usual morphologic features of acute myelomonocytic leukemia.
- Eosinophils at all stages of maturation are usually increased.
- Eosinophilic granules at the promyelocyte and myelocyte stages are larger than usual and often have a purple-violet color. They may be so dense as to obscure the nucleus.
- Mature eosinophils may occasionally show nuclear hyposegmentation.
- Abnormal eosinophils are not usually seen in the peripheral blood.
- Auer rods may be present in myeloblasts.
- Occasional cases do not have eosinophilia or exhibit only myeloid maturation without a monocytic component or only monocytic maturation.
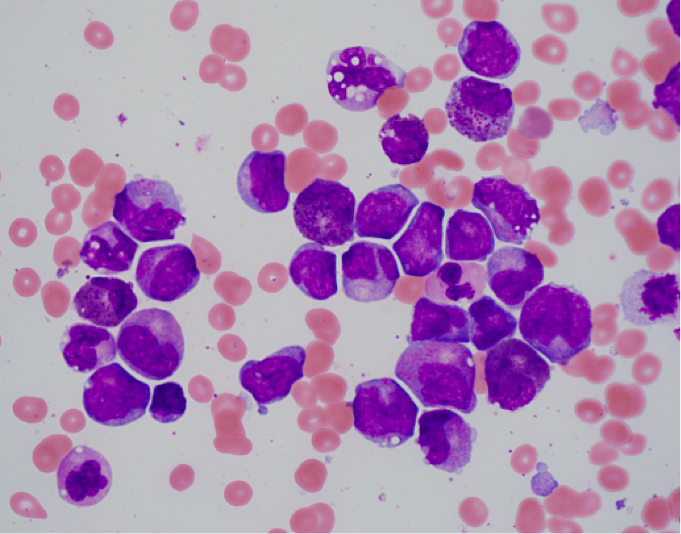
The immunophenotype of this disease is detailed below:
- Naphthol-ASD-chloroacetate esterase reaction, which is negative in normal eosinophils, is faintly positive in the abnormal eosinophils.
- ≥3% of blasts show myeloperoxidase activity.
- Monoblasts and promonoblasts usually show non-specific esterase activity.
Often a complex immunophenotype with multiple blast populations is seen in:
- immature blasts with high CD34 and CD117 expression
- populations with granulocytic differentiation positive for CD13, CD33, CD15, CD65 and MPO
- populations with monocytic differentiation, positive for CD14, CD4, CD11c, CD11b, CD11c, CD64, CD36 and lysozyme
Links
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/cytogenetics-in-acute-myeloid-leukemia
http://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/gene_symbol_report?hgnc_id=HGNC:1539
http://www.clevelandclinicmeded.com.
References
- ↑ Arber, Daniel A.; et al. (2022-09-15). "International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data". Blood. 140 (11): 1200–1228. doi:10.1182/blood.2022015850. ISSN 0006-4971. PMC PMC9479031 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 35767897 Check|pmid=value (help).CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Paschka, Peter; et al. (2006-08-20). "Adverse prognostic significance of KIT mutations in adult acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16) and t(8;21): a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study". Journal of Clinical Oncology: Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 24 (24): 3904–3911. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.9500. ISSN 1527-7755. PMID 16921041.
- ↑ Senapati, Jayastu; et al. (2023-03). "Common kinase mutations do not impact optimal molecular responses in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia treated with fludarabine, cytarabine, and G‐CSF based regimens". American Journal of Hematology. 98 (3). doi:10.1002/ajh.26811. ISSN 0361-8609. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Yoon, J.-H.; et al. (2014-12). "Identification of molecular and cytogenetic risk factors for unfavorable core-binding factor-positive adult AML with post-remission treatment outcome analysis including transplantation". Bone Marrow Transplantation. 49 (12): 1466–1474. doi:10.1038/bmt.2014.180. ISSN 1476-5365. PMID 25111512. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ 5.0 5.1 Solh, Melhem; et al. (2014-12). "Core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia: Heterogeneity, monitoring, and therapy". American Journal of Hematology. 89 (12): 1121–1131. doi:10.1002/ajh.23821. ISSN 1096-8652. PMID 25088818. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Paschka, Peter; et al. (2013-01-03). "Secondary genetic lesions in acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16) or t(16;16): a study of the German-Austrian AML Study Group (AMLSG)". Blood. 121 (1): 170–177. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-05-431486. ISSN 1528-0020. PMID 23115274.
- ↑ Opatz, Sabrina; et al. (2013-09-05). "Exome sequencing identifies recurring FLT3 N676K mutations in core-binding factor leukemia". Blood. 122 (10): 1761–1769. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-01-476473. ISSN 1528-0020. PMID 23878140.
- ↑ Huang, Kezhi; et al. (2016-04). "Leukemogenic potency of the novel FLT3-N676K mutant". Annals of Hematology. 95 (5): 783–791. doi:10.1007/s00277-016-2616-z. ISSN 1432-0584. PMID 26891877. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Cher, C. Y.; et al. (07 08, 2016). "Next-generation sequencing with a myeloid gene panel in core-binding factor AML showed KIT activation loop and TET2 mutations predictive of outcome". Blood Cancer Journal. 6 (7): e442. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.51. ISSN 2044-5385. PMC 5030377. PMID 27391574. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Park, Sang Hyuk; et al. (2015-05). "Incidences and Prognostic Impact of c-KIT, WT1, CEBPA, and CBL Mutations, and Mutations Associated With Epigenetic Modification in Core Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Multicenter Study in a Korean Population". Annals of Laboratory Medicine. 35 (3): 288–297. doi:10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.288. ISSN 2234-3814. PMC 4390696. PMID 25932436. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ 11.0 11.1 Allen, C.; et al. (2013-09). "The importance of relative mutant level for evaluating impact on outcome of KIT, FLT3 and CBL mutations in core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia". Leukemia. 27 (9): 1891–1901. doi:10.1038/leu.2013.186. ISSN 1476-5551. PMID 23783394. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Downing, James R. (2003-02). "The core-binding factor leukemias: lessons learned from murine models". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 13 (1): 48–54. doi:10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00018-7. ISSN 0959-437X. PMID 12573435. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Boddu, Prajwal; et al. (2018-06-08). "Response kinetics and factors predicting survival in core-binding factor leukemia". Leukemia. 32 (12): 2698–2701. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0158-1. ISSN 0887-6924.
- ↑ Yin, John A. Liu; et al. (2012-10-04). "Minimal residual disease monitoring by quantitative RT-PCR in core binding factor AML allows risk stratification and predicts relapse: results of the United Kingdom MRC AML-15 trial". Blood. 120 (14): 2826–2835. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-06-435669. ISSN 0006-4971.
- ↑ Arber, Daniel A.; et al. (05 19, 2016). "The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia". Blood. 127 (20): 2391–2405. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544. ISSN 1528-0020. PMID 27069254. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Marlton, P.; et al. (1995-02-01). "Molecular characterization of 16p deletions associated with inversion 16 defines the critical fusion for leukemogenesis". Blood. 85 (3): 772–779. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 7833479.
- ↑ Martinet, D.; et al. (1997-07). "Detection of 16 p deletions by FISH in patients with inv(16) or t(16;16) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML)". Leukemia. 11 (7): 964–970. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2400681. ISSN 0887-6924. PMID 9204976. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Yang, Richard K.; et al. (2021-10-26). "CBFB Break-Apart FISH Testing: An Analysis of 1629 AML Cases with a Focus on Atypical Findings and Their Implications in Clinical Diagnosis and Management". Cancers. 13 (21): 5354. doi:10.3390/cancers13215354. ISSN 2072-6694. PMC 8582369 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 34771519 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Lv, Lili; et al. (2020). "Acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13.1q22) and deletion of the 5'MYH11/3'CBFB gene fusion: a report of two cases and literature review". Molecular Cytogenetics. 13: 4. doi:10.1186/s13039-020-0474-9. ISSN 1755-8166. PMC 6990480. PMID 32015759 Check
|pmid=value (help). - ↑ Kelly, Johanna; et al. (2005-10-15). "3'CBFbeta deletion associated with inv(16) in acute myeloid leukemia". Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics. 162 (2): 122–126. doi:10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2005.03.001. ISSN 0165-4608. PMID 16213359.
- ↑ Tang, Guilin; et al. (2022-04). "3'CBFB deletion in CBFB-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia retains morphological features associated with inv(16), but patients have higher risk of relapse and may require stem cell transplant". Annals of Hematology. 101 (4): 847–854. doi:10.1007/s00277-022-04767-1. ISSN 1432-0584. PMID 35184217 Check
|pmid=value (help). Check date values in:|date=(help)
Notes
*Primary authors will typically be those that initially create and complete the content of a page. If a subsequent user modifies the content and feels the effort put forth is of high enough significance to warrant listing in the authorship section, please contact the CCGA coordinators (contact information provided on the homepage). Additional global feedback or concerns are also welcome.
Edited by: Fabiola Quintero-Rivera 7/21/2018
*Citation of this Page: “Acute myeloid leukaemia with CBFB::MYH11 fusion”. Compendium of Cancer Genome Aberrations (CCGA), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), updated 07/3/2025, https://ccga.io/index.php/HAEM5:Acute_myeloid_leukaemia_with_CBFB::MYH11_fusion.