HAEM5:Acute myeloid leukaemia with DEK::NUP214 fusion: Difference between revisions
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
Bailey.Glen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Bailey.Glen (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Acute myeloid leukaemia with DEK::NUP214 fusion}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Acute myeloid leukaemia with DEK::NUP214 fusion}} | ||
[[HAEM5:Table_of_Contents|Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)]] | [[HAEM5:Table_of_Contents|Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)]] | ||
==Primary Author(s)*== | ==Primary Author(s)*== | ||
Jennelle C. Hodge, PhD, FACMG | Jennelle C. Hodge, PhD, FACMG | ||
==WHO Classification of Disease== | ==WHO Classification of Disease== | ||
| Line 36: | Line 28: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Related Terminology== | ==Related Terminology== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
|Acceptable | |Acceptable | ||
| | |Acute myeloid leukaemia with t(6;9)(p22.3;q34.1) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Not Recommended | |Not Recommended | ||
| | |N/A | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Gene Rearrangements== | ==Gene Rearrangements== | ||
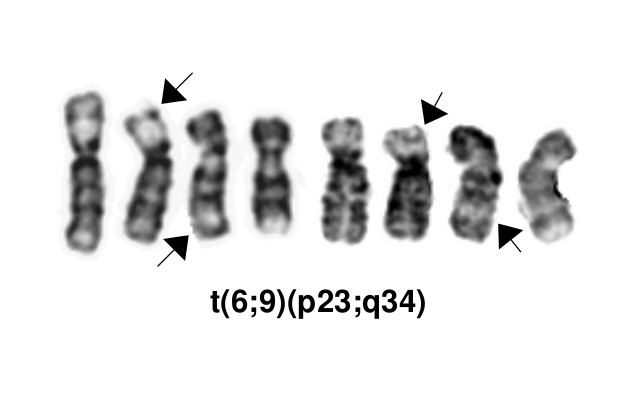
[[File:T(6;9)(p23;q34).png]] | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 73: | Line 50: | ||
!Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |''DEK'' | ||
|''DEK::NUP214''||The pathogenic derivative is the der(6) resulting in fusion of the proto-oncogene 5’ ''DEK'' and 3’''NUP214''(''CAN'').||t(6;9)(p23;q34.1) | |||
|Rare (AML) | |||
|D, P | |||
|Yes (WHO) | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | | | ||
*This AML subtype is classified based on the presence of a t(6;9)(p23;q34.1), which results in fusion of the 5’ portion of ''DEK'' at “6p23” (specifically 6p22.3[hg38]) and the 3’ portion of ''NUP214''(''CAN'') at “9q34.1” (specifically 9q34.13[hg38])<ref name=":0">WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, eds, WHO Classification of Tumours, Haematolymphoid Tumours, 5th edition, IARC Press:Lyon, 2024. Online at: [https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/welcome/ WHO Classification of Tumours].</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Khoury|first=Joseph D.|last2=Solary|first2=Eric|last3=Abla|first3=Oussama|last4=Akkari|first4=Yassmine|last5=Alaggio|first5=Rita|last6=Apperley|first6=Jane F.|last7=Bejar|first7=Rafael|last8=Berti|first8=Emilio|last9=Busque|first9=Lambert|date=2022-07|title=The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms|url=https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35732831|journal=Leukemia|volume=36|issue=7|pages=1703–1719|doi=10.1038/s41375-022-01613-1|issn=1476-5551|pmc=9252913|pmid=35732831}}</ref>. The breakpoints are intronic, producing an in-frame fusion<ref>{{Cite journal|last=von Lindern|first=M.|last2=Fornerod|first2=M.|last3=van Baal|first3=S.|last4=Jaegle|first4=M.|last5=de Wit|first5=T.|last6=Buijs|first6=A.|last7=Grosveld|first7=G.|date=1992|title=The translocation (6;9), associated with a specific subtype of acute myeloid leukemia, results in the fusion of two genes, dek and can, and the expression of a chimeric, leukemia-specific dek-can mRNA|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1549122|journal=Molecular and Cellular Biology|volume=12|issue=4|pages=1687–1697|doi=10.1128/mcb.12.4.1687|issn=0270-7306|pmc=PMC369612|pmid=1549122}}</ref>. The ''DEK''-''NUP214'' fusion present on the derivative chromosome 6 is considered the pathogenic entity as the reciprocal ''NUP214''-''DEK'' fusion on chromosome 9 does not appear to be transcribed<ref>{{Cite journal|last=von Lindern|first=M.|last2=Fornerod|first2=M.|last3=Soekarman|first3=N.|last4=van Baal|first4=S.|last5=Jaegle|first5=M.|last6=Hagemeijer|first6=A.|last7=Bootsma|first7=D.|last8=Grosveld|first8=G.|date=1992|title=Translocation t(6;9) in acute non-lymphocytic leukaemia results in the formation of a DEK-CAN fusion gene|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1308167|journal=Bailliere's Clinical Haematology|volume=5|issue=4|pages=857–879|doi=10.1016/s0950-3536(11)80049-1|issn=0950-3536|pmid=1308167}}</ref>. | |||
*Typically, the ''DEK''-''NUP214'' fusion presents as the sole abnormality but can be part of a complex karyotype<ref name=":0" />. | |||
*Cases with the 6;9 translocation and <20% blasts are not currently classified as AML, which is controversial. Such cases should have close follow-up to monitor for development of more definitive evidence of AML or may be treated as AML if clinically appropriate<ref name=":0" />. | |||
*The t(6;9) occurs in 0.6-1.7% of AML cases in children<ref name=":1" /> (REFERENCES) and about 1% of adult AML cases (REFERENCES). | |||
*''DEK''::''NUP214'' has traditionally been associated with a poor prognosis in both adult and pediatric AML cases<ref name=":0" />. Of note, a 2014 retrospective analysis suggests a better outcome for pediatric patients with this translocation than previously reported<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal|last=Sandahl|first=Julie Damgaard|last2=Coenen|first2=Eva A.|last3=Forestier|first3=Erik|last4=Harbott|first4=Jochen|last5=Johansson|first5=Bertil|last6=Kerndrup|first6=Gitte|last7=Adachi|first7=Souichi|last8=Auvrignon|first8=Anne|last9=Beverloo|first9=H. Berna|date=2014|title=t(6;9)(p22;q34)/DEK-NUP214-rearranged pediatric myeloid leukemia: an international study of 62 patients|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24441146|journal=Haematologica|volume=99|issue=5|pages=865–872|doi=10.3324/haematol.2013.098517|issn=1592-8721|pmc=4008104|pmid=24441146}}</ref>. Elevated white blood cell counts and higher bone marrow blast percentages are associated with shorter periods of overall survival and disease-free survival, respectively<ref name=":0" />. Limited data suggests early allogeneic stem cell transplantation may be associated with better overall survival compared to patients without transplantation, suggesting accurate diagnosis for these patients is crucial<ref name=":0" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Slovak|first=M. L.|last2=Gundacker|first2=H.|last3=Bloomfield|first3=C. D.|last4=Dewald|first4=G.|last5=Appelbaum|first5=F. R.|last6=Larson|first6=R. A.|last7=Tallman|first7=M. S.|last8=Bennett|first8=J. M.|last9=Stirewalt|first9=D. L.|date=2006|title=A retrospective study of 69 patients with t(6;9)(p23;q34) AML emphasizes the need for a prospective, multicenter initiative for rare 'poor prognosis' myeloid malignancies|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16628187|journal=Leukemia|volume=20|issue=7|pages=1295–1297|doi=10.1038/sj.leu.2404233|issn=0887-6924|pmid=16628187}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Ishiyama|first=K.|last2=Takami|first2=A.|last3=Kanda|first3=Y.|last4=Nakao|first4=S.|last5=Hidaka|first5=M.|last6=Maeda|first6=T.|last7=Naoe|first7=T.|last8=Taniguchi|first8=S.|last9=Kawa|first9=K.|date=2012|title=Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia with t(6;9)(p23;q34) dramatically improves the patient prognosis: a matched-pair analysis|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21869835|journal=Leukemia|volume=26|issue=3|pages=461–464|doi=10.1038/leu.2011.229|issn=1476-5551|pmid=21869835}}</ref>. | |||
*The concurrent presence of FLT3-ITD does not appear to negatively impact survival in the pediatric population<ref name=":0" />. | |||
|} | |} | ||
==Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH== | ==Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Chr #!! | !Chr #!!Gain, Loss, Amp, LOH!!Minimal Region Cytoband and/or Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build; Size]!!Relevant Gene(s) | ||
! | !Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | ||
! | !Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | ||
! | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |N/A | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 215: | Line 80: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns== | ==Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Chromosomal Pattern | !Chromosomal Pattern | ||
!Molecular Pathogenesis | !Molecular Pathogenesis | ||
! | !Prevalence - | ||
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | |||
! | !Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | ||
! | !Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | ||
! | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |N/A | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 261: | Line 99: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)== | ==Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)== | ||
*COSMIC does not have specific information on mutations related to this subtype of AML. | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Gene!! | !Gene!!Genetic Alteration!!Tumor Suppressor Gene, Oncogene, Other!!Prevalence - | ||
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | |||
! | !Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | ||
! | !Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | ||
! | !Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |''FLT3'' | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| | |ITD mutations | ||
| | |Oncogene | ||
| | |Common (AML with DEK::NUP214 fusion) | ||
|<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> T | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> T | ||
|<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Yes (NCCN) | |<span class="blue-text">EXAMPLE:</span> Yes (NCCN) | ||
| | | | ||
*FLT3-ITD occurs in 69% of children and 78% of adults. | |||
*In contrast to FLT3-ITD mutations, FLT3-TKD is very uncommon. | |||
*The concurrent presence of FLT3-ITD with t(6;9) does not appear to negatively impact survival in the pediatric population<ref name=":0" />. | |||
|}Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in [https://www.cbioportal.org/ <u>cBioportal</u>], [https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic <u>COSMIC</u>], and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content. | |}Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in [https://www.cbioportal.org/ <u>cBioportal</u>], [https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic <u>COSMIC</u>], and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content. | ||
==Epigenomic Alterations== | ==Epigenomic Alterations== | ||
| Line 343: | Line 129: | ||
==Genes and Main Pathways Involved== | ==Genes and Main Pathways Involved== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Gene; Genetic Alteration!!Pathway!!Pathophysiologic Outcome | !Gene; Genetic Alteration!!Pathway!!Pathophysiologic Outcome | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |''DEK::NUP214'' | ||
|< | |Unknown | ||
| | |The fusion protein is known to act as an aberrant transcription factor, alter nuclear transport and induce myeloid cell-specific global protein synthesis<ref name=":0" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Ageberg|first=Malin|last2=Drott|first2=Kristina|last3=Olofsson|first3=Tor|last4=Gullberg|first4=Urban|last5=Lindmark|first5=Anders|date=2008|title=Identification of a novel and myeloid specific role of the leukemia-associated fusion protein DEK-NUP214 leading to increased protein synthesis|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18181180|journal=Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer|volume=47|issue=4|pages=276–287|doi=10.1002/gcc.20531|issn=1098-2264|pmid=18181180}}</ref>. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
==Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods== | ==Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods== | ||
Karyotype, FISH, RT-PCR | Karyotype, FISH, RT-PCR (and any other fusion detecting technologies) | ||
==Familial Forms== | ==Familial Forms== | ||
| Line 394: | Line 156: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:07, 3 July 2025
Haematolymphoid Tumours (WHO Classification, 5th ed.)
Primary Author(s)*
Jennelle C. Hodge, PhD, FACMG
WHO Classification of Disease
| Structure | Disease |
|---|---|
| Book | Haematolymphoid Tumours (5th ed.) |
| Category | Myeloid proliferations and neoplasms |
| Family | Acute myeloid leukaemia |
| Type | Acute myeloid leukaemia with defining genetic abnormalities |
| Subtype(s) | Acute myeloid leukaemia with DEK::NUP214 fusion |
Related Terminology
| Acceptable | Acute myeloid leukaemia with t(6;9)(p22.3;q34.1) |
| Not Recommended | N/A |
Gene Rearrangements
| Driver Gene | Fusion(s) and Common Partner Genes | Molecular Pathogenesis | Typical Chromosomal Alteration(s) | Prevalence -Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEK | DEK::NUP214 | The pathogenic derivative is the der(6) resulting in fusion of the proto-oncogene 5’ DEK and 3’NUP214(CAN). | t(6;9)(p23;q34.1) | Rare (AML) | D, P | Yes (WHO) |
|
Individual Region Genomic Gain/Loss/LOH
| Chr # | Gain, Loss, Amp, LOH | Minimal Region Cytoband and/or Genomic Coordinates [Genome Build; Size] | Relevant Gene(s) | Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A |
Characteristic Chromosomal or Other Global Mutational Patterns
| Chromosomal Pattern | Molecular Pathogenesis | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A |
Gene Mutations (SNV/INDEL)
- COSMIC does not have specific information on mutations related to this subtype of AML.
| Gene | Genetic Alteration | Tumor Suppressor Gene, Oncogene, Other | Prevalence -
Common >20%, Recurrent 5-20% or Rare <5% (Disease) |
Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Significance - D, P, T | Established Clinical Significance Per Guidelines - Yes or No (Source) | Clinical Relevance Details/Other Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLT3
|
ITD mutations | Oncogene | Common (AML with DEK::NUP214 fusion) | EXAMPLE: T | EXAMPLE: Yes (NCCN) |
|
Note: A more extensive list of mutations can be found in cBioportal, COSMIC, and/or other databases. When applicable, gene-specific pages within the CCGA site directly link to pertinent external content.
Epigenomic Alterations
Not applicable
Genes and Main Pathways Involved
| Gene; Genetic Alteration | Pathway | Pathophysiologic Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| DEK::NUP214 | Unknown | The fusion protein is known to act as an aberrant transcription factor, alter nuclear transport and induce myeloid cell-specific global protein synthesis[1][8]. |
Genetic Diagnostic Testing Methods
Karyotype, FISH, RT-PCR (and any other fusion detecting technologies)
Familial Forms
Not applicable
Additional Information
Not applicable
Links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, eds, WHO Classification of Tumours, Haematolymphoid Tumours, 5th edition, IARC Press:Lyon, 2024. Online at: WHO Classification of Tumours.
- ↑ Khoury, Joseph D.; et al. (2022-07). "The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms". Leukemia. 36 (7): 1703–1719. doi:10.1038/s41375-022-01613-1. ISSN 1476-5551. PMC 9252913 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 35732831 Check|pmid=value (help). Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ von Lindern, M.; et al. (1992). "The translocation (6;9), associated with a specific subtype of acute myeloid leukemia, results in the fusion of two genes, dek and can, and the expression of a chimeric, leukemia-specific dek-can mRNA". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 12 (4): 1687–1697. doi:10.1128/mcb.12.4.1687. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 369612. PMID 1549122.CS1 maint: PMC format (link)
- ↑ von Lindern, M.; et al. (1992). "Translocation t(6;9) in acute non-lymphocytic leukaemia results in the formation of a DEK-CAN fusion gene". Bailliere's Clinical Haematology. 5 (4): 857–879. doi:10.1016/s0950-3536(11)80049-1. ISSN 0950-3536. PMID 1308167.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Sandahl, Julie Damgaard; et al. (2014). "t(6;9)(p22;q34)/DEK-NUP214-rearranged pediatric myeloid leukemia: an international study of 62 patients". Haematologica. 99 (5): 865–872. doi:10.3324/haematol.2013.098517. ISSN 1592-8721. PMC 4008104. PMID 24441146.
- ↑ Slovak, M. L.; et al. (2006). "A retrospective study of 69 patients with t(6;9)(p23;q34) AML emphasizes the need for a prospective, multicenter initiative for rare 'poor prognosis' myeloid malignancies". Leukemia. 20 (7): 1295–1297. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2404233. ISSN 0887-6924. PMID 16628187.
- ↑ Ishiyama, K.; et al. (2012). "Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia with t(6;9)(p23;q34) dramatically improves the patient prognosis: a matched-pair analysis". Leukemia. 26 (3): 461–464. doi:10.1038/leu.2011.229. ISSN 1476-5551. PMID 21869835.
- ↑ Ageberg, Malin; et al. (2008). "Identification of a novel and myeloid specific role of the leukemia-associated fusion protein DEK-NUP214 leading to increased protein synthesis". Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer. 47 (4): 276–287. doi:10.1002/gcc.20531. ISSN 1098-2264. PMID 18181180.
Notes
*Primary authors will typically be those that initially create and complete the content of a page. If a subsequent user modifies the content and feels the effort put forth is of high enough significance to warrant listing in the authorship section, please contact the Associate Editor or other CCGA representative. When pages have a major update, the new author will be acknowledged at the beginning of the page, and those who contributed previously will be acknowledged below as a prior author.
Prior Author(s):
*Citation of this Page: “Acute myeloid leukaemia with DEK::NUP214 fusion”. Compendium of Cancer Genome Aberrations (CCGA), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), updated 07/3/2025, https://ccga.io/index.php/HAEM5:Acute_myeloid_leukaemia_with_DEK::NUP214_fusion.